Ilustratīvs attēls
OK, something of a teaser since, obviously, there is no easy way to do this. But if Latvia was more like Lithuania, this might have been possible.
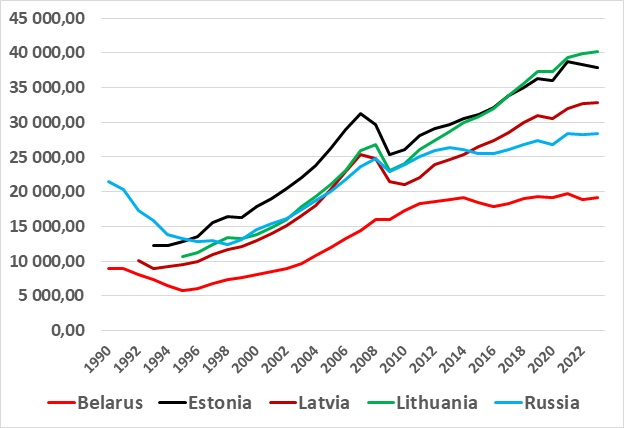
Latvian economic development hasn’t been poor since independence – far from – but the star performer is Lithuania. In Figure 1 I show GDP per capita as a measure for income per person for the three Baltic countries and for Russia and Belarus in constant prices. The following can be observed or calculated:
- By 2018 Lithuania overtook Estonia in income per person.
- From 2015 Latvia has been ahead of Russia and the gap has increased to 15.5%.
- But Lithuania is another 22.4% ahead of Latvia – and a staggering 100% ahead of Belarus! Choosing, as the latter did, to be just an appendix to the Russian economy does not seem to be such a good idea…
It can also be seen that Latvia and Lithuania were basically neck-and-neck in 2006 but since then the afore-mentioned gap of 22.4% has developed. Average annual growth in income per person in Latvia since 2006 has been 2.1% but in Lithuania 3.3%, in both cases dragged down by the financial crisis of course, but a good example of the power of exponential growth. A mere 1.2 percentage point difference results in a significant 22.4% difference within 17 years. Should Latvia e.g. grow by two percentage points faster per year than Lithuania – which nothing indicates that it will – it would take 10 years to catch up.
Figure 1: GDP per capita, constant USD, PPS adjusted, Baltics, Belarus and Russia, early 1990s – 2023
Source: IMF; 2023 data are obviously estimates
A different way to compare Latvia and Lithuania is presented in Figure 2, which shows the simple ratio of Lithuanian GDP per capita to the Latvian ditto.
We see that Lithuania was always ahead of Latvia (also seen from Figure 1) but that the difference narrowed until 2006 after which it grew again. Part of the explanation must be that Latvia had a bigger boom before the financial crisis but also a worse aftermath following this crisis – but there must also be other, more structural factors, present to explain why Lithuania “just” diverged from the Latvian growth performance.
Figure 2: Lithuanian GDP per capita as share of Latvian GDP per capita
Source: IMF and own calculations
And then to the headline of this column. The Ministry of Finance, in its most recent Stability Programme (p. 29) estimates GDP for 2023 at 43.6 bill. EUR.
Now some back-of-the-envelope calculations: Had Latvia been on par with Lithuania, i.e. had closed the 22.4% gap, GDP would have been 9.8 bill. EUR bigger. Since taxes, roughly, are one third of GDP in Latvia, this would have contributed some 3.2 bill. EUR extra in tax revenue for a budget that is burdened by spending demands from health, teachers, military, Ukrainian refugees etc.
Or, in short, just another way of arguing why economic growth – or the lack thereof – is so important.
But let me finish on a more positive note: Russian GDP is forecast by the IMF to reach 154 trillion rubles in 2023. If Russia were like Lithuania its GDP would be 41% bigger (= 64 trillion rubles) – but Russia is not like Lithuania, thus this amount, equivalent to a staggering 636 bill. EUR is not available for its war effort in Ukraine. At times, though seldom, lack of economic growth is a positive thing.
Morten Hansen is Head of Economics Department at Stockholm School of Economics in Riga and former Vice-Chairman at the Fiscal Discipline Council of Latvia